Saffron is a perennial plant which has an onion. It grows in southwestern Asia, south Spain and southern parts of Europe. It has a stem, six purple petals and three strands of red stigmas. Saffron as a spice, has various forms such as saffron powder, Negin, Sargol,Pushal, Bunch and Konj which is mostly used for adding color and odor to meals, desserts and drinks in food industry.
After harvesting from the fields, saffron transfers to laboratories for physical, chemical and microbiological tests and standard quality assessments. In laboratory, specialists examine the following factors :
• Extraction and color detection of additives via HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography)
• Color strength test and determination of Crocin, Safranal and Picrocrocin
• Moisture and volatiles in saffron
• Whole ash in saffron
• Insoluble ashes in acid
• External materials related to the plant and the environment
• Solubility of the extract in cold water
Saffron reduces blood fat and cholesterol. Saffron is sedative, appetizing, and antispasmodic; it prevents heart diseases and cancer, strengthens memory and lowers blood pressure. Saffron is used for treating asthma, skin and eye diseases, urinary tract infections, jaundice, premature menstruation, bloating, stomachache and anemia. Saffron helps digestion and strengthens the stomach. It is also used as a painkiller, especially for gum pain.
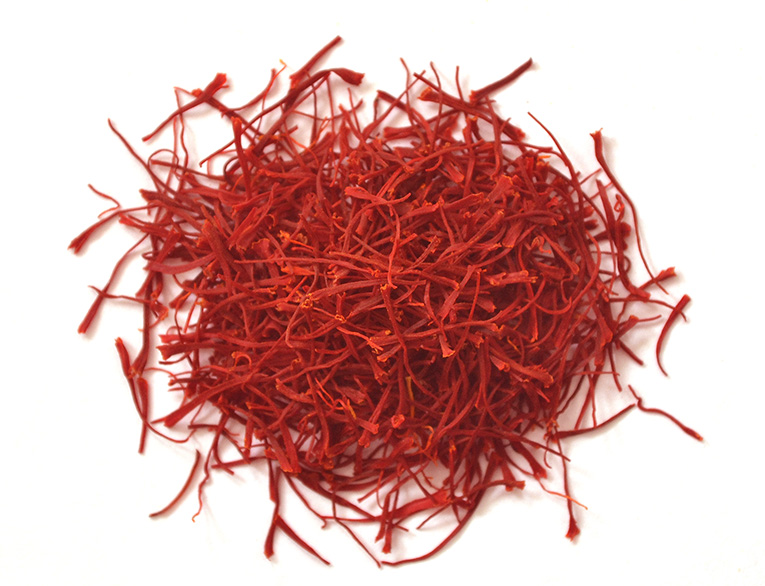

Allred (Sargol)

Bunch

Pushal
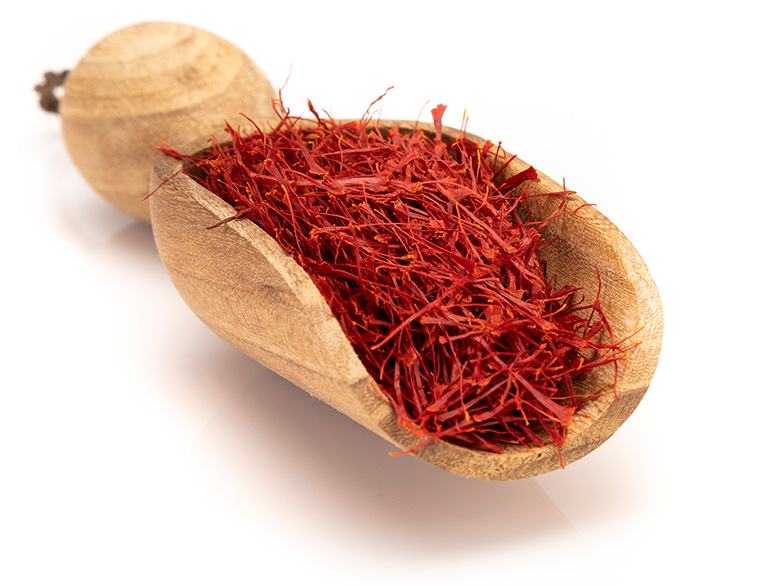

Negin
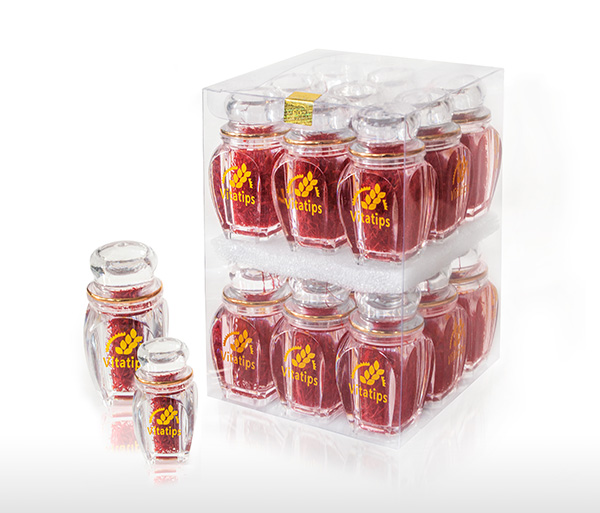
Glass (Exclusive)
Negin : 1-1.5 gr
Allred : 2 gr
Pushal : 1 gr
No in each carton : 12 * 24 Pcs

Khatam
Negin : 0.5 gr
Allred : 0.5-1 gr
Pushal : 0.5 gr
Powder : 0.5-1 gr
No in each carton : 30 * 12 Pcs
Negin : 1 gr
Allred : 2 gr
Pushal : 1 gr
Powder : 4-5 gr
No in each carton : 21 * 10 Pcs
Crystal
Negin : 1 gr
Allred : 2-3 gr
Pushal : 1 gr
Bunch : 1 gr
No in each carton : 8 * 12 Pcs
Negin : 2-3 gr
Allred : 5 gr
Pushal : 2-3 gr
Bunch : 2 gr
No in each carton : 16 * 12 Pcs


Bulk
500 gr
No in each mother box : 8 Pcs (only for Germany)
No in each mother box : 16 Pcs (for other countries)
Crystal With Cover
X Small No.1
Negin : 0.5 gr
Allred : 0.5-1 gr
Pushal : 1 gr
No in each carton: 12 * 18 Pcs
Small No.2
Negin : 1 gr
Allred : 2-3 gr
Pushal : 1 gr
Bunch : 1 gr
No in each carton: 12 * 18 Pcs

